It goes without saying that our society is moving faster than it ever has in the past. As medical technology surges forward with unprecedented speed and accuracy, many of us are left in the ensuing dust storm of obsolete procedures that were commonplace mere decades ago. But if we look up and gaze into the near future, we can see the beginnings of a whole new world of medical treatments that the doctors of yesterday couldn’t even begin to imagine.
Let's take a look at the top 10 Future Technologies in the Medical Field:
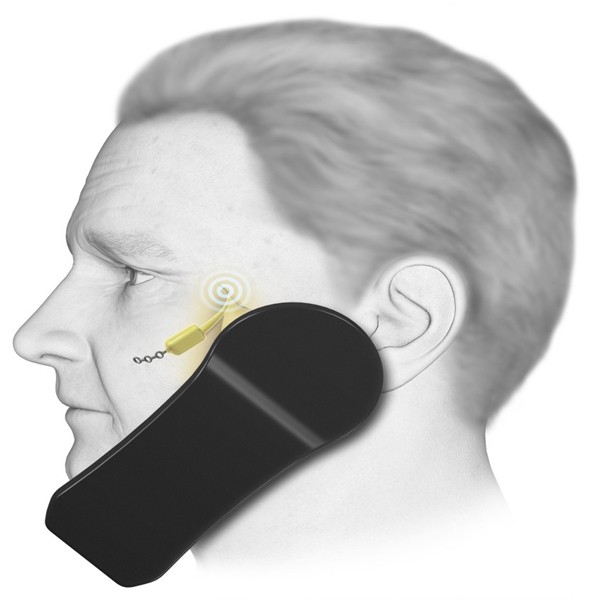
1. Electronic Aspirin
A lot of people have been suffering from chronic forms of a headache and they have been advised to take two aspirins by most of the doctors, but this method has turned out to be useless and it only works in the short term. For that reason, a clinical investigation has been performed on a technology that is used for blocking the signals that identify the occurrence of a headache. The system involves implanting a small nerve permanently that’s function is to stimulate the device located in the upper gum on the side of the head that gets affected by a headache. The tip of the implant gets connected with the nerve bundles, so when the patient starts sensing the beginning of a headache, they place an RC on the cheek that is nearer to the implant; this will result in blocking the neurotransmitters that cause the pain in the first place.
2. Magnetic Levitation
Artificial lung tissue grown with magnetic levitation: it sounds like something out of science fiction, and it was, until now. In 2010, Glauco Souza and his team began looking into a way to create realistic human tissue using nanomagnets that allowed lab-grown tissue to levitate above a nutrient solution.The result was the most realistic synthetically grown organ tissue ever grown. Typically, lab-grown tissue is created in a petri dish, but elevating the tissue allows it to grow in a 3D shape that allows for more complex cell layers. That 3D growth pattern is a more perfect simulation of the way cells grow in the human body, which means that this is a huge step forward in creating artificial organs that can be transplanted into humans.
3. Digital Diagnostics
Since health care could be a burden for those who are not able to easily move and visit a doctor, digital diagnostics have been taking place to make things easier for elders and disabled people. There has been one device of this digital diagnostics that is already out there and it is the Neurotrack. This device can be used for testing and diagnose Alzheimer; it detects the damages that may occur on the hippocampus- the first part of the brain that is usually affected by this disease- and evaluate the movement of the eye.

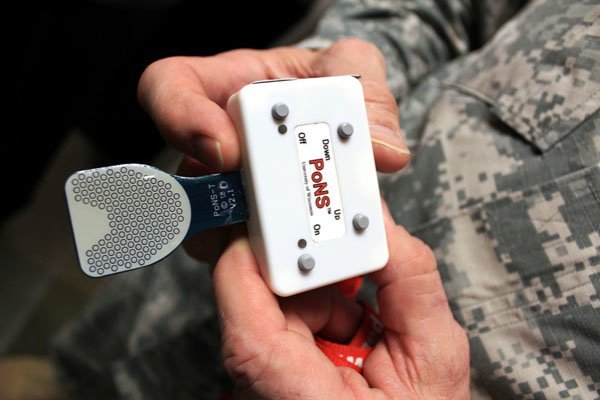
4. Brain Damage Repair
The brain is a delicate organ, and even slight trauma can have lasting effects if it’s bumped in the wrong places. For people with traumatic brain injury, extensive rehabilitation is pretty much the only hope of leading a normal life again. Alternatively, they could just get a zap on the tongue.Your tongue is connected to the nervous system through thousands of nerve clusters, some of which lead directly into the brain. Based on that fact, the Portable NeuroModulation Stimulator, or PoNS, stimulates specific nerve regions on the tongue to hopefully focus the brain on repairing the nerves that were damaged. And so far, it works. Patients being treated with that type of neuromodulation showed vast improvement after only a week. Fair warning, you might get brain damage just trying to read that link.Apart from blunt trauma, the PoNS could feasibly be used to repair the brain from anything, including alcoholism, Parkinson’s, strokes, and multiple sclerosis.

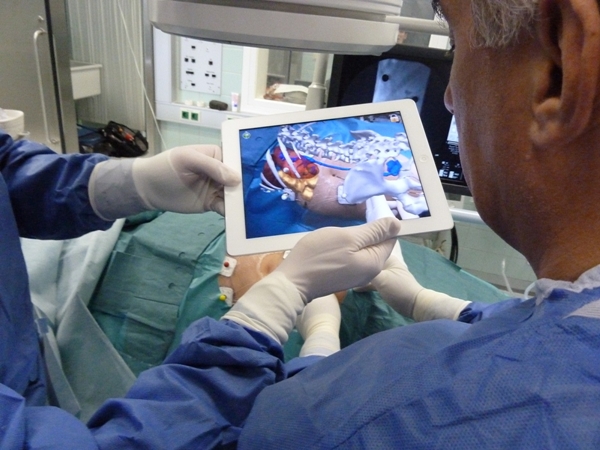
5. Augmented Reality
The Augmented Reality is a new technology used to create an image generated by a computer, allowing it to be viewed in the person’s real world, providing a complex view. This method is still going through strong testing, but it is expected to enter the market very soon, for it seems very beneficial for the patients, for it allows the surgeons to see through bodily structures such as blood vessels in a specific organ without having to open it, resulting in a more precise elimination. A clinic located in Germany has already started to attempt the application of the augmented reality on iPads in the OR.
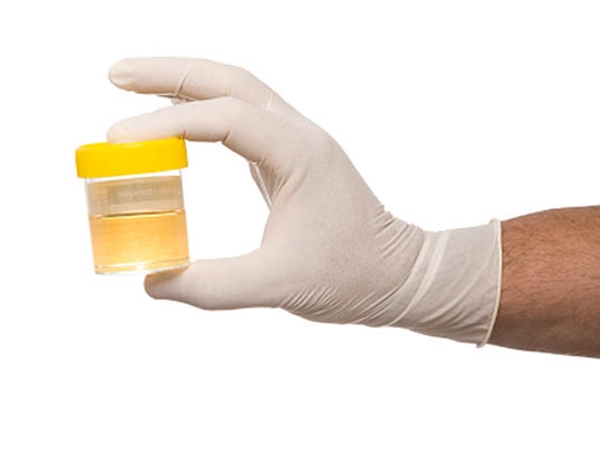
6. Brain Cells from Urine
In a sentence we won’t get to use often, researchers have turned pee into human brain cells. At the Guangzhou Institute of Biomedicine and Health in China, biologists have taken waste cells from urine and modified them with the use of retroviruses to create progenitor cells, which the body uses as the building blocks for brain cells. The most valuable benefit to this method is that the new neurons created haven’t caused tumors in any of the mice used for testing.See, embryonic stem cells have been used for this in the past, but one of their side effects was that they were more likely to develop tumors after transplant. But after only a few weeks, the pee-based cells had already begun to shape into neurons with absolutely no unwanted mutations.The obvious medical benefit of getting cells from urine is that, well, it’s freely available, and scientists could work on developing neurons that are sourced from the same person, increasing the chance that they’ll be accepted by the body.
7. Robot Assistants
Yes, Robots have already made a great appearance in sci-fi movies and they have told us several times that the world is expected to be controlled by technology someday soon, but this time, things are getting real. The world is developing rapidly and robots are highly expected to invade the world of medicine to work as assistants which can take care of elder patients as their numbers are increasing on a daily basis. In California, there has been a robot made by a company as a model, designing it to be able to find veins in the patient’s arm and take blood samples out of it. On the other hand, Japan has also created a cartoonish version of this robot shaped as a huge bear to be able to carry patients and move them from one place to another, especially those who are disabled and use wheelchairs. These robots are strong devices that are designed to carry up to almost 450 kilograms and they are specifically made to be used at homes for patients who need assistance.

8. Artificial Cell Mimicry
It’s obvious that the direction of medical technology is leaning more towards reproducing human tissue outside the body, allowing us to create “spare parts,” so to speak. If one organ isn’t working, we can just replace it with a new one, fresh off the assembly line. Now that idea is moving down to the cellular level with a gel that mimics the action of specific cells.The material is formed in bunches that are only 7.5 billionths of a meter wide—for comparison, that’s about four times wider than a DNA double helix. Cells have their own type of skeleton, known as a cytoskeleton, which is made of proteins. The synthetic gel will take the place of that cytoskeleton in a cell, and when it’s applied to, say, a wound, it replaces any cells that were lost or damaged. In a practical sense, it would work like a tiny, tiny sewer grate. Fluids can pass through the cell, which allow the wound to continue healing, but the artificial skeleton prevents bacteria from passing through with the fluid.
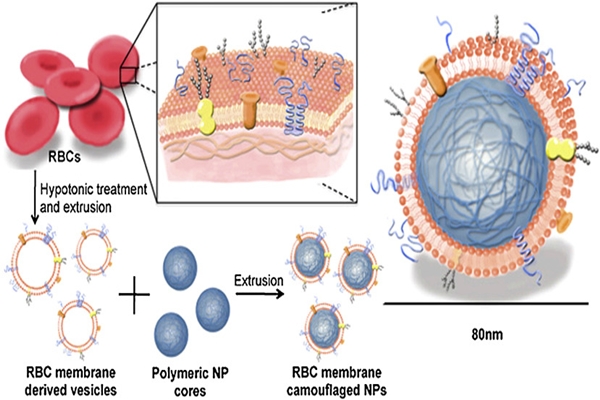
9. Growing Organs in Labs
Since the beginning of time, a lot of humans have gone through organ failures; as a result, they need new organs to be transplanted for them, but they are probably placed on a waiting list until the right match is found. New technologies are expected to solve this problem by restoring the function of the failed organs or by growing organs in labs. The latter can be done by using the stem cells of the patient to grow an organ that works perfectly for their bodies. The whole idea still sounds surreal for a lot of people, but it is expected to take place anytime soon and that would save more people in a shorter time.
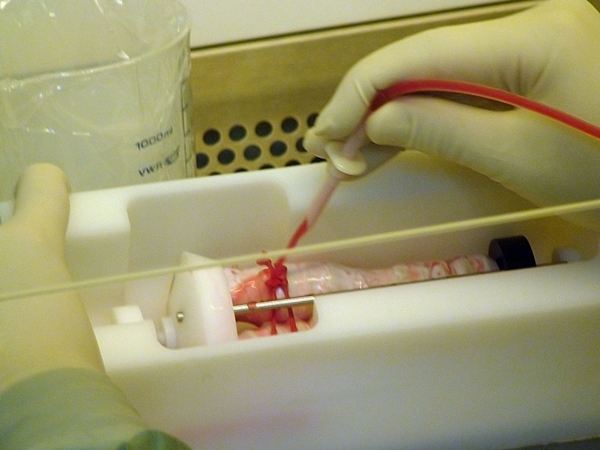
10. Printed Bones
Remember the days when you would break your arm and then have to wear a cast for weeks while the bone naturally healed itself? It looks like those days are behind us. Using 3D printers, researchers at Washington State University have developed a hybrid material that has the same properties the same strength and flexibility as real bone.This “model” can then be placed in the body at the site of the fracture while the real bone grows up and around it like a scaffolding. Once the process is complete, the model disintegrates. The printer they’re using is a ProMetal 3D printer consumer technology available to anyone with enough cash. It was the material for the bone structure that was the real problem, but they’ve created a formula that uses a combination of zinc, silicon, and calcium phosphate that works well so well, in fact, that the entire process has already been successfully tested in rabbits. When the bone material was combined with stem cells, the natural bone grew back much faster than normal.The real benefit of this technology is that, feasibly, any tissue even full organs could be grown with 3D printers once we have the right combination of starting materials.