A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, and so forth. A notational symbol that represents a number is called a numeral. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, the term number may refer to a symbol, a word, or a mathematical abstraction.
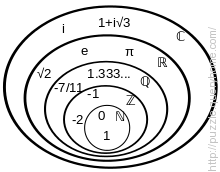
Main number systems
\mathbb{N} Natural= 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ... or 1, 2, 3, 4, ...
\mathbb{Z} Integer =..., −5, −4, −3, −2, −1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ...
\mathbb{Q} Rational =a/b
where a and b are integers and b is not 0
\mathbb{R} Real=The limit of a convergent sequence of rational numbers
\mathbb{C} Complex=a + bi where a and b are real numbers and i is the square root of −1