he source qualifier transformation is an active,connected transformation used to represent the rows that the integrations service reads when it runs a session. You need to connect the source qualifier transformation to the relational or flat file definition in a mapping. The source qualifier transformation converts the source data types to the Informatica native data types. So, you should not alter the data types of the ports in the source qualifier transformation.
The source qualifier transformation is used to do the following tasks:
- Joins: You can join two or more tables from the same source database. By default the sources are joined based on the primary key-foreign key relationships. This can be changed by explicitly specifying the join condition in the "user-defined join" property.
- Filter rows: You can filter the rows from the source database. The integration service adds a WHERE clause to the default query.
- Sorting input: You can sort the source data by specifying the number for sorted ports. The Integration Service adds an ORDER BY clause to the default SQL query
- Distinct rows: You can get distinct rows from the source by choosing the "Select Distinct" property. The Integration Service adds a SELECT DISTINCT statement to the default SQL query.
- Custom SQL Query: You can write your own SQL query to do calculations.
Creating Source Qualifier Transformation:
The easiest method to create a source qualifier transformation is to drag the source definition in to a mapping. This will create the source qualifier transformation automatically.
Follow the below steps to create the source qualifier transformation manually.
- Click Transformation -> Create.
- Select the Source Qualifier transformation.
- Enter a name for the transformation
- Click on create.
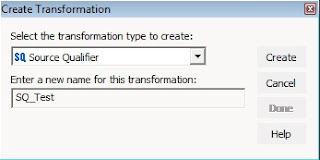
- Select a source, click OK and then click Done.
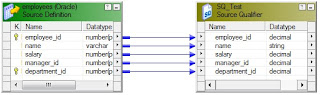
Now you can see in the below image how the source qualifier transformation is connected to the source definition.
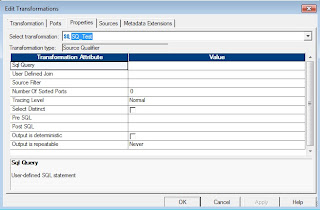
Source Qualifier Transformation Properties:
We can configure the following source qualifier transformation properties on the properties tab. To go to the properties tab, open the source qualifier transformation by double clicking on it and then click on the properties tab.
| Property |
Description |
| SQL Query |
To specify a custom query which replaces the default query. |
| User-Defined Join |
Condition used for joining multiple sources. |
| Source Filter |
Specifies the filter condition the Integration Service applies when querying rows. |
| Number of Sorted Ports |
Used for sorting the source data |
| Tracing Level |
Sets the amount of detail included in the session log when you run a session containing this transformation. |
| Select Distinct |
To select only unique rows from the source. |
| Pre-SQL |
Pre-session SQL commands to run against the source database before the Integration Service reads the source. |
| Post-SQL |
Post-session SQL commands to run against the source database after the Integration Service writes to the target. |
| Output is Deterministic |
Specify only when the source output does not change between session runs. |
| Output is Repeatable |
Specify only when the order of the source output is same between the session runs. |
Note: For flat file source definitions, all the properties except the Tracing level will be disabled.
To Understand the following, Please create the employees and departments tables in the source and emp_dept table in the target database.
create table DEPARTMENTS
(
DEPARTMENT_ID NUMBER(4) not null,
DEPARTMENT_NAME VARCHAR2(15) not null,
MANAGER_ID NUMBER(6)
);
create table EMPLOYEES
(
EMPLOYEE_ID NUMBER(6) not null,
NAME VARCHAR2(10),
SALARY NUMBER(10,2),
MANAGER_ID NUMBER(6),
DEPARTMENT_ID NUMBER(4)
);
create table EMP_DEPT
(
EMPLOYEE_ID NUMBER(6) not null,
NAME VARCHAR2(10),
SALARY NUMBER(10,2),
MANAGER_ID NUMBER(6),
DEPARTMENT_ID NUMBER(4),
DEPARTMENT_NAME VARCHAR2(15) not null
);
Viewing the Default Query or Generating the SQL query:
For relational sources, the Integration Service generates a query for each Source Qualifier transformation when it runs a session. To view the default query generated, just follow the below steps:
- Go to the Properties tab, select "SQL Query" property. Then open the SQL Editor, select the "ODBC data source" and enter the username, password.
- Click Generate SQL.
- Click Cancel to exit.
The default query generated in this case is
SELECT employees.employee_id,
employees.name,
employees.salary,
employees.manager_id,
employees.department_id
FROM employees
You can write your own SQL query rather than relaying the default query for performing calculations.
Note: You can generate the SQL query only if the output ports of source qualifier transformation is connected to any other transformation in the mapping. The SQL query generated contains only the columns or ports which are connected to the downstream transformations.
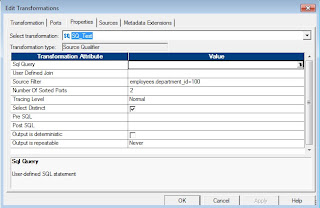
Specifying the "Source Filter, Number Of Sorted Ports and Select Distinct" properties:
Follow the below steps for specifying the filter condition, sorting the source data and for selecting the distinct rows.
- Go to the properties tab.
- Select "Source Filter" property, open the editor and enter the filter condition (Example: employees.department_id=100) and click OK.
- Go to the "Number Of Sorted Ports" property and enter a value (Example: 2). This value (2) means to sort the data on the first two ports in the source qualifier transformation.
- Tick the check box for the "Select Distinct" property.
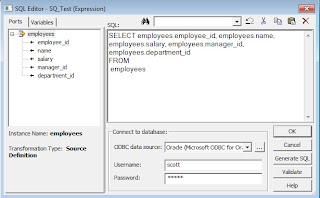
Now follow the steps for "Generating the SQL query" and generate the SQL query. The SQL query generated is
SELECT DISTINCT employees.employee_id,
employees.name,
employees.salary,
employees.manager_id,
employees.department_id
FROM employees
WHERE employees.department_id=100
ORDER BY employees.employee_id, employees.name
Observe the DISTINCT, WHERE and ORDER BY clauses in the SQL query generated. The order by clause contains the first two ports in the source qualifier transformation. If you want to sort the data on department_id, salary ports; simply move these ports to top position in the source qualifier transformationa and specify the "Number Of Sorted Ports" property as 2
Joins:
The SQL transformation can be used to join sources from the same database. By default it joins the sources based on the primary-key, foreign-key relationships. To join heterogeneous sources, use Joiner Transformation.
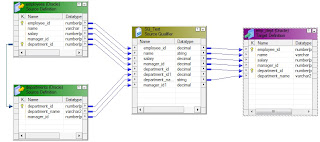
A foreign-key is created on the department_id column of the employees table, which references the primary-key column, department_id, of the departments table.
Follow the below steps to see the default join
Create only one source qualifier transformation for both the employees and departments.
Go to the properties tab of the source qualifier transformation, select the "SQL QUERY" property and generate the SQL query.
The Generated SQL query is
SELECT employees.employee_id,
employees.name,
employees.salary,
employees.manager_id,
employees.department_id,
departments.department_name
FROM employees,
departments
WHERE departments.department_id=employees.department_id
You can see the employees and departments tables are joined on the department_id column in the WHERE clause.
There might be case where there won't be any relationship between the sources. In that case, we need to override the default join. To do this we have to specify the join condition in the "User Defined Join" Property. Using this property we can specify outer joins also. The join conditions entered here are database specific.
As an example, if we want to join the employees and departments table on the manager_id column, then in the "User Defined Join" property specify the join condition as "departments.manager_id=employees.manager_id". Now generate the SQL and observe the WHERE clause.
Pre and Post SQL:
You can add the Pre-SQL and Post-SQL commands. The integration service runs the Pre-SQL and Post-SQL before and after reading the source data respectively.
