Hi Harshita,
First of all thanks to you for this wonderful question, which encourage me to look into this new concept. After reading from net I found the below information which I would like to share with Queryhome community.
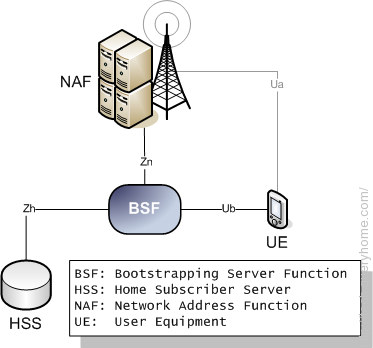
The above information can be found from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bootstrapping_Server_Function
Introduction
A Bootstrapping Server Function (BSF) is an intermediary element in Cellular networks which provides application independent functions for mutual authentication of user equipment and servers unknown to each other and for 'bootstrapping' the exchange of secret session keys afterwards.
GBA/GAA Setup
The setup and function to deploy a generic security relation as described is called Generic Bootstrapping Architecture (GBA) or Generic Authentication Architecture (GAA). In short, it consists of the following elements.
- user equipment (UE), e. g. a mobile cellular telephone; needs access
to a specific service
- application server (NAF: Network Application Function), e. g. for
mobile TV; provides the service
- BSF (Bootstrapping Server Function); arranges security relation
between UE and NAF
- mobile network operator's Home Subscriber Server (HSS); hosts user
profiles.
In this case, the term 'bootstrapping' is related to building a security relation with a previously unknown device first and to allow installing security elements (keys) in the device and the BSF afterwards.
Workflow
The BSF is introduced by the application server (NAF), after an unknown UE device is trying to get service access: the NAF refers the UE to the BSF. UE and BSF mutually authenticate via 3GPP protocol AKA (Authentication and Key Agreement); additionally, the BSF sends related queries to the Home Subscriber Server (HSS). Afterwards, UE and BSF agree on a session key to be used for encrypted data exchange with the application server (NAF). When the UE again connects to the NAF, the NAF is able to obtain the session key as well as user specific data from the BSF and can start data exchange with the end device (UE), using the related session keys for encryption.
Thanks,
Chinmoy
