Standard Date and Time Format Specifiers
A Date and time format specifier is a special character that enables you to display the date and time values in different formats. For example, you can display a date in mm-dd-yyyy format and time in hh:mm format. If you are displaying GMT time as the output, you can display the GMT time along with the abbreviation GMT using date and time format specifiers.
The date and time format specifiers allow you to display the date and time and time in 12-hour and 24-hour formats.
The following is the syntax for date and time format specifiers.
Console.WriteLine(“{format specifier}”, <datetime object>);
Where,
Format specifier: Is the date and time format specifier.
Datetime object: Is the object of the DateTime class.
Some Standard date and time specifiers are used in the Console.WriteLine() method with the datetime object. To create the datetime object, you must create an object of the DateTime class and initialize it. The formatted date and time are always displayed as string in the console window.
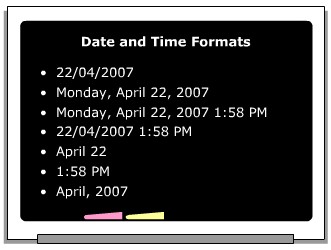
The table shown below displays some of the standard date and time format specifiers in C#.
Format Specifier | Name | Description |
D | Long date | Displays date in long date pattern. The default format is “dddd*, MMMM*, dd, yyyy”. |
d | Short date | Displays date in short date pattern. The default format is “mm/dd/yyyy” |
f | Full date/time (short time) | Displays date in long date and short time patterns,, separated by a space. The default format is “dddd*”, MMMM* dd, yyyy HH*:mm*”. |
F | Full date/time (long time) | Displays date in long date and long time patterns, separated by a space. The default format is “dddd*, MMMM* dd,,yyyy HH*: mm*: ss*”. |
G | General date/time (short time) | Displays date in short date and short time patterns, separated by a space. The default format is “MM/dd/yyyy HH*:mm*”. |
The following snippet demonstrates the conversion of a specified date and time using the d,D,f,F and g date and time format specifiers:-
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
//Returns short date (MM/DD/YYYY)
Console.WriteLine("Short date format (d): {0:d}",dt);
//Returns long date (Day, Month Date, Year)
Console.WriteLine("Long date format (D) : {0:D}", dt);
//Returns full date with time and without seconds
Console.WriteLine("Full date with time without seconds (f) : {0:f}", dt);
//Returns full date with time and with seconds
Console.WriteLine ("Full date with time with seconds (F) : {0:F}", dt);
//Returns short date and short time without seconds
Console.WriteLine ("Short date and short time without seconds (g) : {0:g}", dt);
Output:
Short date format (d) : 23/06/2017
Long date format (D) : Friday, June 23, 2017
Full date with time without seconds (f) : Friday, June 23, 2017 11:12 AM
Full date with time with seconds (F): Friday, June 23, 2017 11:12:34 AM
Short date and short time without seconds (g): 23/06/2017 11:12 AM
More Standard Date and Time Format Specifiers
| Format | Specifier Name | Description |
| G | General date/time (long time) Displays date in short date and long time patterns, separated by a space. | The default format is "MM/dd/yyyy HH*:mm*:ss*". |
| m or M | Month day Displays only month and day of the date. | The default format is "MMMM* dd". |
| t | Short time Displays time in short time pattern. | The default format is "HH*:mm*". |
| T | Long time Displays time in long time pattern. | The default format is "HH*:mm*:ss*". |
| y or Y | Year month pattern Displays only month and year from the date. | he default format is "YYYY MMMM*". |
| | | |
The following snippet demonstrates the conversion of a specified date and time using the G,m,t,T :-
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
//Returns short date and short time with seconds
Console.WriteLine ("Short date and short time with seconds (G) : {0:G}",dt);
//Returns month and day -M can also be used
Console.WriteLine ("Month and day (m) : {0:m}", dt);
//Returns short time
Console.WriteLine("Short time (t) : {0:t}", dt);
//Returns short time with seconds
Console.WriteLine("Short time with seconds (T) : {0:T}", dt);
//Returns year and month -Y also can be used
Console.WriteLine ("Year and Month (y): {0:y}" dt);
Output:
Short date and short time with seconds (G): 23/06/2017 11:40:55 AM
Month and day (m) : June 23
Short time (t) : 11:40 AM
Short time with seconds (T): 11:40:55 AM
Year and Month (y): June , 2017
