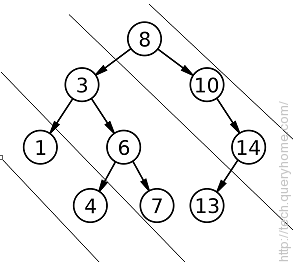
Inputs : shown in Image.
Output :
Diagonal Traversal of binary tree :
8 10 14
3 6 7 13
1 4
---Sample Code---
// C++ program for diagnoal traversal of Binary Tree
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Tree node
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *left, *right;
};
/* root - root of the binary tree
d - distance of current line from rightmost
-topmost slope.
diagonalPrint - multimap to store Diagonal
elements (Passed by Reference) */
void diagonalPrintUtil(Node* root, int d,
map<int, vector<int>> &diagonalPrint)
{
// Base case
if (!root)
return;
// Store all nodes of same line together as a vector
diagonalPrint[d].push_back(root->data);
// Increase the vertical distance if left child
diagonalPrintUtil(root->left, d + 1, diagonalPrint);
// Vertical distance remains same for right child
diagonalPrintUtil(root->right, d, diagonalPrint);
}
// Print diagonal traversal of given binary tree
void diagonalPrint(Node* root)
{
// create a map of vectors to store Diagonal elements
map<int, vector<int> > diagonalPrint;
diagonalPrintUtil(root, 0, diagonalPrint);
cout << "Diagonal Traversal of binary tree : \n";
for (auto it = diagonalPrint.begin();
it != diagonalPrint.end(); ++it)
{
for (auto itr = it->second.begin();
itr != it->second.end(); ++itr)
cout << *itr << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
}
// Utility method to create a new node
Node* newNode(int data)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(8);
root->left = newNode(3);
root->right = newNode(10);
root->left->left = newNode(1);
root->left->right = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(14);
root->right->right->left = newNode(13);
root->left->right->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right->right = newNode(7);
diagonalPrint(root);
return 0;
}
