Selection Sort:-
Selection sort is a simple sorting algorithm. This sorting algorithm is an in-place comparison-based algorithm in which the list is divided into two parts, the sorted part at the left end and the unsorted part at the right end. Initially, the sorted part is empty and the unsorted part is the entire list.The smallest element is selected from the unsorted array and swapped with the leftmost element, and that element becomes a part of the sorted array. This process continues moving unsorted array boundary by one element to the right.
This process continues and requires n−1 passes to sort n items, since the final item must be in place after the (n−1) st pass.
This algorithm is not suitable for large data sets as its average and worst case complexities are of Ο(n2), where n is the number of items.
Algorithm:-
Step 1 − Set MIN to location 0
Step 2 − Search the minimum element in the list
Step 3 − Swap with value at location MIN
Step 4 − Increment MIN to point to next element
Step 5 − Repeat until list is sorted.
Pictorial Representation:-
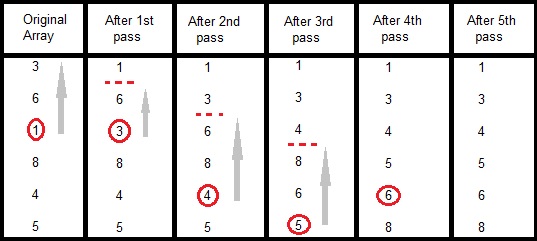
In the first pass, the smallest element found is 1, so it is placed at the first position, then leaving first element, smallest element is searched from the rest of the elements, 3 is the smallest, so it is then placed at the second position. Then we leave 1 and 3, from the rest of the elements, we search for the smallest and put it at third position and keep doing this, until array is sorted.
C program for selection sort:-
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 7
int intArray[MAX] = {4,6,3,2,1,9,7};
void printline(int count) {
int i;
for(i = 0;i <count-1;i++) {
printf("=");
}
printf("=\n");
}
void display() {
int i;
printf("[");
// navigate through all items
for(i = 0;i<MAX;i++) {
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
}
void selectionSort() {
int indexMin,i,j;
// loop through all numbers
for(i = 0; i < MAX-1; i++) {
// set current element as minimum
indexMin = i;
// check the element to be minimum
for(j = i+1;j<MAX;j++) {
if(intArray[j] < intArray[indexMin]) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
if(indexMin != i) {
printf("Items swapped: [ %d, %d ]\n" , intArray[i], intArray[indexMin]);
// swap the numbers
int temp = intArray[indexMin];
intArray[indexMin] = intArray[i];
intArray[i] = temp;
}
printf("Iteration %d#:",(i+1));
display();
}
}
main() {
printf("Input Array: ");
display();
printline(50);
selectionSort();
printf("Output Array: ");
display();
printline(50);
}
Complexity:-
| Algorithm |
Worst case |
Average case |
Best case |
| Bubble sort |
O(n2) |
O(n2) |
O(n2)
|
Its worst case would be when the array is in reversed order. In that case, it would perform O(n2).
For average case too its performance is O(n2).
