Introduction
A database is a systematic collection of data. A Database Management System (DBMS) is required to store, access, delete, or otherwise organize data in a database.
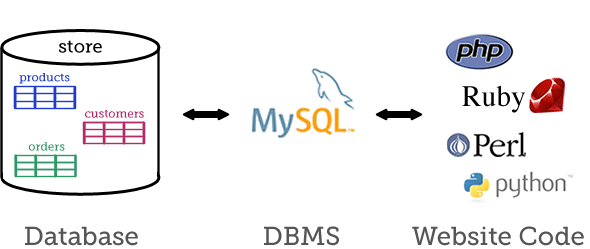
MySQL is an open source DBMS. It is easy to download, modify, and use open source software without having to pay and fees or royalty to the original author.

DBMS helps you to manage data in two ways:
- It provides an interface to manage data.
- It supports connectivity to other applications that can be used to manage data.
Both, DBMS and RDBMS, perform the same task of storing and managing data. One of the key differences between DBMS and RDBMS is that RDBMS splits large amount of data into smaller tables and establishes relationship between the tables. DBMS stores large amount of data in a single table. Also, the RDBMS is based on a relational model whereas DBMS is not.
MySQL is an open source RDBMS. MySQL uses the standardized Structured Query Language (SQL) to manage the database. MySQL is developed and distributed by MySQL AB, a company founded by the MySQL developers. In 2008, Sun Microsystem acquired MySQL AB. In 2010, Oracle acquired Sun Microsystems and hence, MySQL is now owned by Oracle Corp.
Features of MySQL
MySQL was designed to achieve speed, robustness, and ease of use. The features of MySQL are as follows:
Technical Features:
- Is written in C and C++
- Is tested with different compilers
- Is compatible with multiple operating systems
- Has Application programming Interfaces (APIs) for accessing MySQL databases available in many languages, including C, C++, Eiffel, Java, Perl, Python, Ruby, and Tcl.
- Is using multiple kernel threads or processing units, if available, for data processing.
- Is using multiple processors where available, boosting performance.
- Has ability to divert memory resources from inactive threads to active threads for faster processing
- Has commands and features to retrieve, update, and delete data from several tables
- Has support for compatibility to be used as a separate application or as an embedded library.
Commands and Functions:
- Has support for all MySQL operators and functions in the SELECT statement and the WHERE clause
- Has support for tables from different database in on statement
- Has support for table and column aliases
- Has support for displaying information about databases, tables, and indexes using the SHOW command
- Has support for displaying query resolution information using the EXPLAIN command
- Has full support for SQL GROUP BY and ORDER BY clauses, group functions and left and right outer joins.
Scalability and Limits:
- Handles large databases that have upto 5 billion rows
- Allows upto 64 indexes per table
- Allows upto 16 keys per table
Connectivity
- Supports connectivity on any platform to MySQL server using Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) sockets
- Supports connectivity on Windows NT, 2000, XP, 2003, and Vista using named pipes or shared-memory connections.
- Supports connectivity on UNIX systems using UNIX domain socket files.
Advantages of MySQL over other RDBMS
There are many commercial Database Management Systems such as Oracle, Microsoft SQL server, and Sybase available in the market. These Database Management systems are robust, reliable, and support most of the features that a user wants. However, it is impossible for these databases to compete with MySQL with regards to price, as MySQL is available for free. In addition, for commercial Database Management Systems, the initial setup cost is most expensive, resource intensive and time consuming whereas with MySQL, this is not the case. This is one of the key advantages of MySQL.
Also, as the source for MySQL is fully available, you can customize MySQL as required. There are many troubleshooting techniques, command help, and syntax help that are available. This information is available in blogs, forums, and lists that do not require paid subscriptions. However, troubleshooting techniques, command help, and syntax help for commercial databases may require a paid subscription.
MySQL provides different versions that work on different versions of Linux, UNIX, Microsoft, Windows, and other operating systems. MySQL also supports various built-in and third-party GUI tools for faster and easier design, implementation, and administration.







