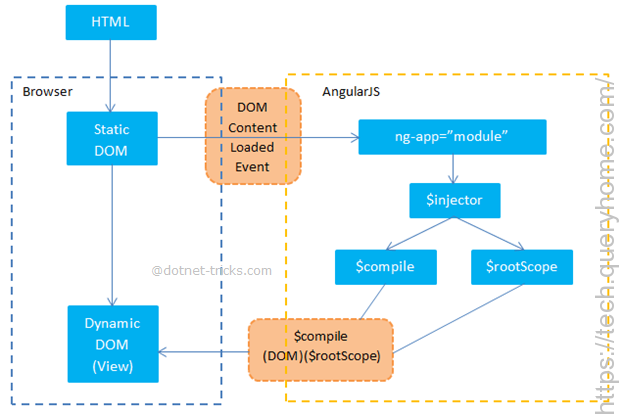
Angular initializes automatically upon DOMContentLoaded event or when the angular.js script is downloaded to the browser and the document.readyState is set to complete. At this point AngularJS looks for the ng-app directive which is the root of angular app compilation and tells about AngularJS part within DOM. When the ng-app directive is found then Angular will:
Load the module associated with the directive.
Create the application injector.
Compile the DOM starting from the ng-app root element.
This process is called auto-bootstrapping.
Hello !
<script src="lib/angular.js"></script>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('Ctrl', function ($scope) {
$scope.msg = 'World';
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Manual Bootstrap Process
You can manually initialized your angular app by using angular.bootstrap() function. This function takes the modules as parameters and should be called within angular.element(document).ready() function. The angular.element(document).ready() function is fired when the DOM is ready for manipulation.
<html>
<body>
<div ng-controller="Ctrl">
Hello !
</div>
<script src="lib/angular.js"></script>
<script>
var app = angular.module('myApp', []);
app.controller('Ctrl', function ($scope) {
$scope.msg = 'World';
});
//manual bootstrap process
angular.element(document).ready(function () {
angular.bootstrap(document, ['myApp']);
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Note
You should not use the ng-app directive when manually bootstrapping your app.
You should not mix up the automatic and manual way of bootstrapping your app.
Define modules, controller, services etc. before manually bootstrapping your app as defined in above example.
