What is Spring MVC?
The Spring Web model-view-controller (MVC) framework is designed around a DispatcherServlet that dispatches requests to handlers, with configurable handler mappings, view resolution, locale and theme resolution as well as support for uploading files.
The default handler is based on the @Controller and @RequestMapping annotations, offering a wide range of flexible handling methods. With the introduction of Spring 3.0, the @Controller mechanism also allows you to create RESTful Web sites and applications, through the @PathVariable annotation and other features.
Spring Web MVC you can use any object as a command or form-backing object; you do not need to implement a framework-specific interface or base class. Spring's data binding is highly flexible: for example, it treats type mismatches as validation errors that can be evaluated by the application, not as system errors.
Thus you need not duplicate your business objects' properties as simple, untyped strings in your form objects simply to handle invalid submissions, or to convert the Strings properly. Instead, it is often preferable to bind directly to your business objects.
Spring's view resolution is extremely flexible. A Controller is typically responsible for preparing a model Map with data and selecting a view name but it can also write directly to the response stream and complete the request. View name resolution is highly configurable through file extension or Accept header content type negotiation, through bean names, a properties file, or even a custom ViewResolver implementation.
The model (the M in MVC) is a Map interface, which allows for the complete abstraction of the view technology. You can integrate directly with template based rendering technologies such as JSP, Velocity and Freemarker, or directly generate XML, JSON, Atom, and many other types of content. The model Map is simply transformed into an appropriate format, such as JSP request attributes, a Velocity template model.
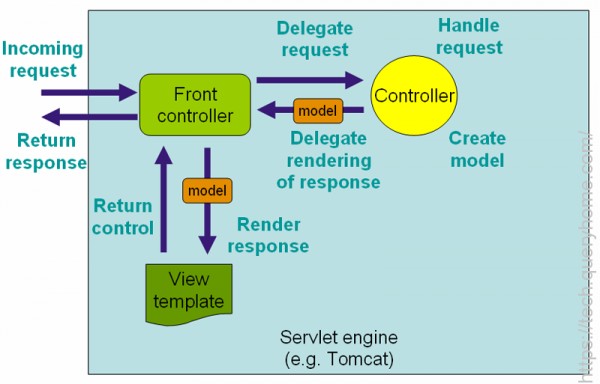
Spring MVC, like many other web frameworks, is designed around the front controller pattern where a central Servlet, the DispatcherServlet, provides a shared algorithm for request processing while actual work is performed by configurable, delegate components. This model is flexible and supports diverse workflows.
The DispatcherServlet, as any Servlet, needs to be declared and mapped according to the Servlet specification using Java configuration or in web.xml. In turn the DispatcherServlet uses Spring configuration to discover the delegate components it needs for request mapping, view resolution, exception handling
Video for Spring MVC
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xrExTCcv5Qg





