LIPA - Local IP Access
SIPTO - Selected IP Traffic Offload.
Where LIPA is used to offload the IP traffic within the enterprise and completely avoiding the mobile core network or external internet for the Data traffic which can be accessed locally and provide the access of the same using the handheld device via Femto or EnodeB.
Whereas SIPTO is used to selectively offload the IP Traffic over internet by avoiding the mobile core network for the Data traffic.
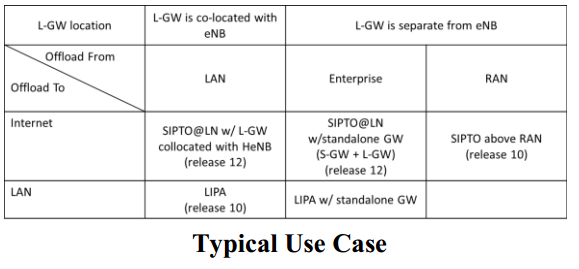
In both the cases IP offloading is achieved by the introduction of LGW and following Table describes the possible architectural scenarios.
Case 1: LIPA
“Local IP Access” is the architecture that HeNB and a Local GW (L-GW) are in the residential/ enterprise IP network and can be achieved using a L-GW colocated with the HeNB.
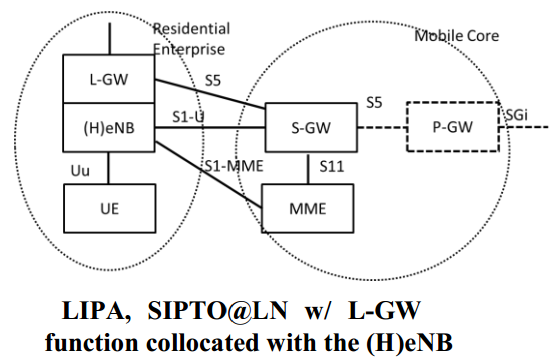
Case 2: SIPTO at the Local Network with L-GW function collocated with the (H)eNB
” SIPTO at the Local Network with L-GW function collocated with the (H)eNB “ is also the architecture that (H)eNB and a L-GW are in the residential/ enterprise IP network and also assumes a L-GW colocated with the (H)eNB. (Refer Figure for Case 1)
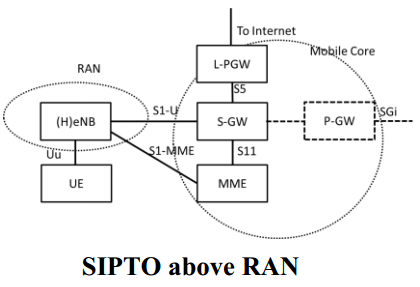
Case 3: SIPTO above RAN
“SIPTO above RAN” is the architecture that assumes both (H)eNB and a L-GW ( or LP-GW) in the mobile operator network.
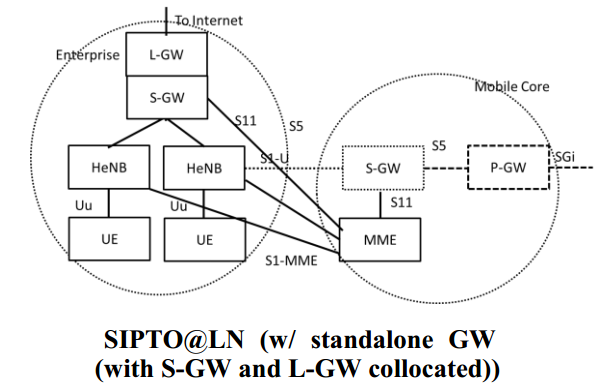
Case 4: SIPTO @LN (SGW and LGW colocated)
In this scenario LGW and eNB/HNB are separate nodes but located into enterprise/residential IP Network.