LTE, the GUTI is the Globally Unique Temporary ID, and identifies the mobile device to the LTE network. The GUTI is assigned to the device by the Mobility Management Entity (MME), the access network’s primary control node. By allocating a temporary ID to the device, the MME maintains the security of the IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identification) when transmitting over radio interface.
Components of the GUTI
MMEI: MME Identifier (Identify a MME uniquely; operator configures in eNB)
MMEGI: MME Group ID (Unique within a PLMN, used to identify different MME Groups)
MMEC: MME Code (Identify a MME uniquely within a MME group)
GUMMEI: Globally Unique MME Identifier globally
M-TMSI: MME-Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity
The GUTI has two parts. These are the globally unique Globally Unique Mobility Management Entity Identifier (GUMMEI), which identifies the network, and the M-TMSI, which identifies the device. The GUMMEI is 42 bits in length and the M-TMSi is 32 bits long.
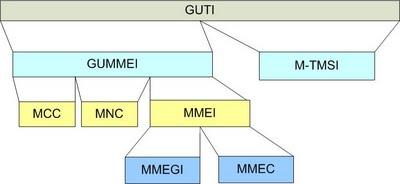
The GUMMEI portion of the GUTI is comprised of several parts. These are the Mobile Network Code (MNC), the Mobile Country Code (MCC), and the MME ID (Mobility Management Entity ID). The Mobility Management Entity is the primary control node for the LTE access network. MMEs are usually clustered in pools, and the
MME ID identifies both the MME pool and the node within that pool.
Where as M-TMSI Identifies the UE within the MME. MME allocates M-TMSI to UE, to make M-TMSI, MME uses the UE IMSI and it changes for a UE, when the UE moves to another MME.
