Bearer is a virtual concept. It defines how the UE data is treated when it travels across the network. Network might treat some data in a special way and treat others normally. In short, bearer is a set of network parameter that defines data specific treatment .
Default Bearer in LTE
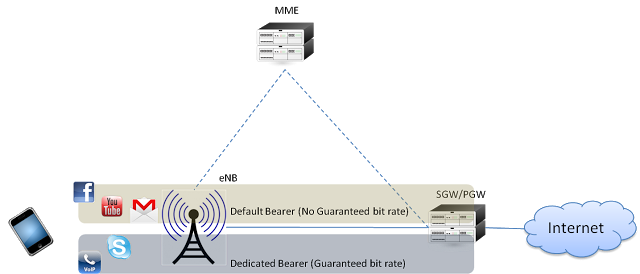
When LTE UE attaches to the network for the first time, it will be assigned default bearer which remains as long as UE is attached. Default bearer is best effort service and comes with an IP address. UE can have additional default bearers as well.
Each default bearer will have a separate IP address. QCI 5 to 9 (Non- GBR) can be assigned to default bearer.
Dedicated Bearer
Dedicated bearers provides dedicated tunnel to one or more specific traffic (i.e. VoIP, video etc). Dedicated bearer acts as an additional bearer on top of default bearer. It does not require separate IP address due to the fact that only additional default bearer needs an IP address and therefore dedicated bearer is always linked to one of the default bearer established previously. Dedicated bearer can be GBR or non-GBR (whereas default bearer can only be non-GBR).
For services like VoLTE we need to provide better user experience and this is where Dedicated bearer would come handy. Dedicated bearer uses Traffic flow templates (TFT) to give special treatment to specific services
