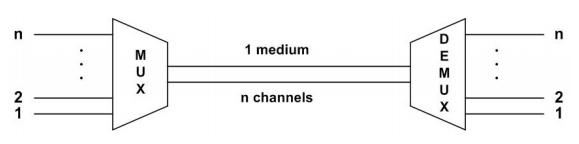
Two nodes to utilize the full capacity the channel uses multiplexing techniques to utilize the full capacity of a data link. Using multiplexing multiple users can share the capacity of a transmission link.
FDM (Frequency-division multiplexing)
In FDM each signal is modulated onto different unique RF carrier frequency and all carrier frequencies are separated significantly so that bandwidth of the signals do not overlap in frequency domain.

Each channel (defined by its center frequency, and its bandwidth) occupies a fraction of the bandwidth of the link. Example: radio and television signal transmission
TDM (Time-division multiplexing)
In TDM, more than one digital signals can be carried on single medium for transmission by interleaving each signals in time. In TDM each channel occupies the entire bandwidth of the link for a very short period of time.
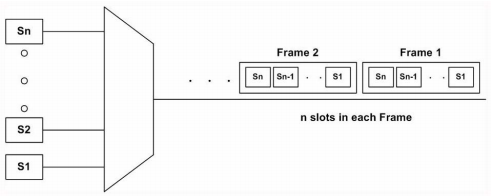
TDM can be of two types 1. Synchronous TDM 2. Statistical TDM
1. Synchronous TDM - time slot are assigned to each channel in a regular sequence
2. Statistical TDM - time slots are assigned to signals as they arrive at the multiplexer
