What is Link List
W linked list is a data structure consisting of a group of nodes which together represent a sequence. Under the simplest form, each node is composed of a data and a link to the next node in the sequence.
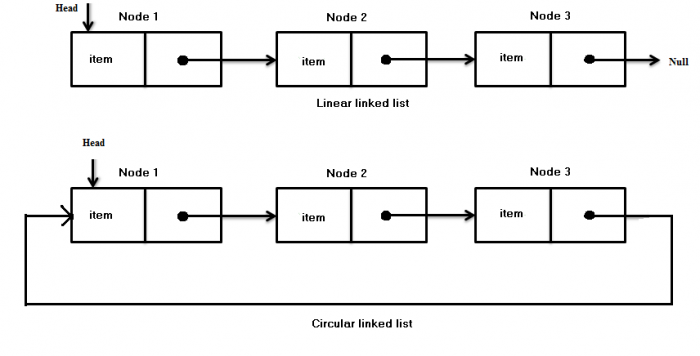
Reversing a LinkList
Reversing a link list can be done in two ways one by swapping the data values and another is by manipulating only the pointers, in this article I am discussing only the pointer manipulation mechanism in recursive and non-recursive ways.
Sample Code
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head;
int length= 0;
int list_size()
{
printf("\n No. of elements in the list: %d", length);
return length;
}
struct node * create_node(int data)
{
struct node *new;
new = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
new->next = null;
new->data = data;
length++;
return new;
}
void add_node(int data)
{
struct node *new;
new = create_node(data);
if (head == NULL)
{
head = new;
}
else
{
new->next = head;
head = new;
}
}
void display_list()
{
struct node *temp_head;
temp_head = head;
if (temp_head == NULL)
{
printf("List is empty");
return;
}
while (temp_head != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", temp_head->data);
temp_head = temp_head->next;
}
}
void reverse_list()
{
struct node *p, *q, *r;
p = q = r = head;
p = p->next->next;
q = q->next;
r->next = NULL;
q->next = r;
while (p != NULL)
{
r = q;
q = p;
p = p->next;
q->next = r;
}
*head = q;
}
void reverse_list_recursion(struct node **phead)
{
// Storing the head into local head variable
struct node *lhead = *phead;
if (lhead && lhead->next) {
*phead = lhead->next;
reverse_list_recursion(phead);
lhead->next->next = lhead;
lhead->next = NULL;
}
}


