TCP/IP means Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. It is the network model used in the current Internet architecture as well.
Protocols are set of rules which govern every possible communication over a network. These protocols describe the movement of data between the source and destination or the internet. These protocols offer simple naming and addressing schemes.
The TCP/IP Model was developed by Department of Defence's Project Research Agency (ARPA, later DARPA) as a part of a research project of network interconnection to connect remote machines.
The features that stood out during the research, which led to making the TCP/IP reference model were:
- Support for a flexible architecture. Adding more machines to a network was easy.
- The network was robust, and connections remained intact untill the source and destination machines were functioning.
The overall idea was to allow one application on one computer to talk to(send data packets) another application running on different computer.
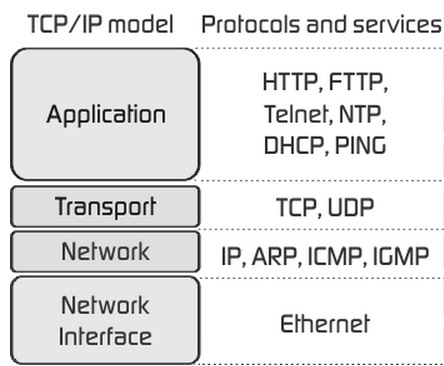
TCI/IP model consists of 4 different layers:
- Network Access Layer.
- Internet Layer.
- Transport Layer.
- Application Layer.
LEVEL 1
Network Access Layer is the first layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. Network Access Layer defines details of how data is physically sent through the network, including how bits are electrically or optically signaled by hardware devices that interface directly with a network medium, such as coaxial cable, optical fiber, or twisted pair copper wire.
The protocols included in Network Access Layer are Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI, X.25, Frame Relay etc.
The most popular LAN architecture among those listed above is Ethernet. Ethernet uses an Access Method called CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access/Collision Detection) to access the media, when Ethernet operates in a shared media. An Access Method determines how a host will place data on the medium.
LEVEL 2
Internet Layer is the second layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. The position of Internet layer is between Network Access Layer and Transport layer. Internet layer pack data into data packets known as IP datagrams, which contain source and destination address (logical address or IP address) information that is used to forward the datagrams between hosts and across networks. The Internet layer is also responsible for routing of IP datagrams.
Packet switching network depends upon a connectionless internetwork layer. This layer is known as Internet layer. Its job is to allow hosts to insert packets into any network and have them to deliver independently to the destination. At the destination side data packets may appear in a different order than they were sent. It is the job of the higher layers to rearrange them in order to deliver them to proper network applications operating at the Application layer.
The main protocols included at Internet layer are IP (Internet Protocol), ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol), ARP (Address Resolution Protocol), RARP (Reverse Address Resolution Protocol) and IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol).
LEVEL 3
Transport Layer is the third layer of the four layer TCP/IP model. The position of the Transport layer is between Application layer and Internet layer. The purpose of Transport layer is to permit devices on the source and destination hosts to carry on a conversation. Transport layer defines the level of service and status of the connection used when transporting data.
The main protocols included at Transport layer are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol).
LEVEL 4
Application layer is the top most layer of four layer TCP/IP model. Application layer is present on the top of the Transport layer. Application layer defines TCP/IP application protocols and how host programs interface with Transport layer services to use the network.
Application layer includes all the higher-level protocols like DNS (Domain Naming System), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), Telnet, SSH, FTP (File Transfer Protocol), TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol), SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) , DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), X Windows, RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) etc.
