Lets first see the handover and then we can see the roaming.
Broadly LTE handover can be classified into four cases -
1. Inter Cell (only cell is changed not the enodeB)
2. Inter EnodeB (enode B is also changed in addition to (1))
3. Inter MME (MME is also changed in addition to (2))
4. Inter RAT (LTE to UMTS)
Now see what is roaming, roaming is a special case of handover where user accesses the home operator's services even while in a visited network.
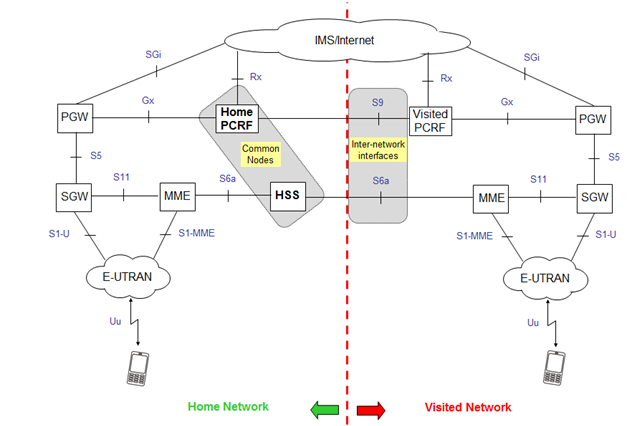
See the following figure of LTE Roaming
In Short IP session is established over home PGW to visited SGW where both signaling and IP traffic is transmitted over S8 interface. The visited EPS network provides access to basing signaling procedures supported by visited MME. Home EPS network enables access to external networks (IMS/Internet). This method is called Home Routed Roaming method.
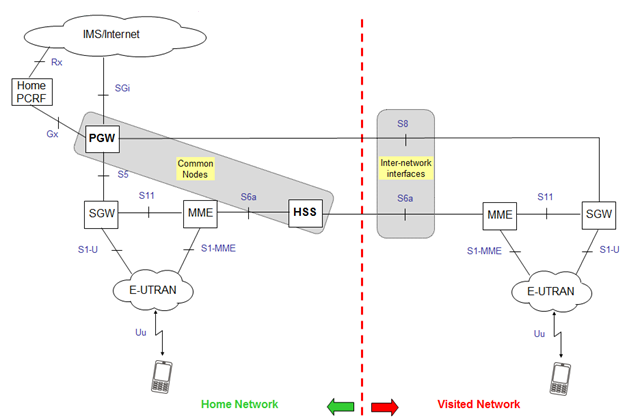
User’s packet routing over his home network may be inefficient especially when visited SGW and home PGW are geographically very far away from each other. For such cases the 3GPP standard also provide optimized packet routing (of the user’s IP traffic) over visited PGW . In this way, also the local traffic can be serviced and this method is called Local Breakout. Local breakout reduces the tariff of roaming as in the home routed roaming case home operator can count the user’s packets and can demand visited network to pay based on usage which is not the case of local breakout. See the architecture -