Consider a scenario when your real program is more then the size of RAM or physical memory then how can you execute such a program. The answer is Virtual Memory.
Virtual memory is simply the operating system using some amount of disk space as if it were real memory or we can say Virtual memory is the separation of user logical memory from physical memory which is stored in the disk. This separation allows an extremely large virtual memory to be provided for programmers when only a smaller physical memory is available.
How Virtual Memory Works
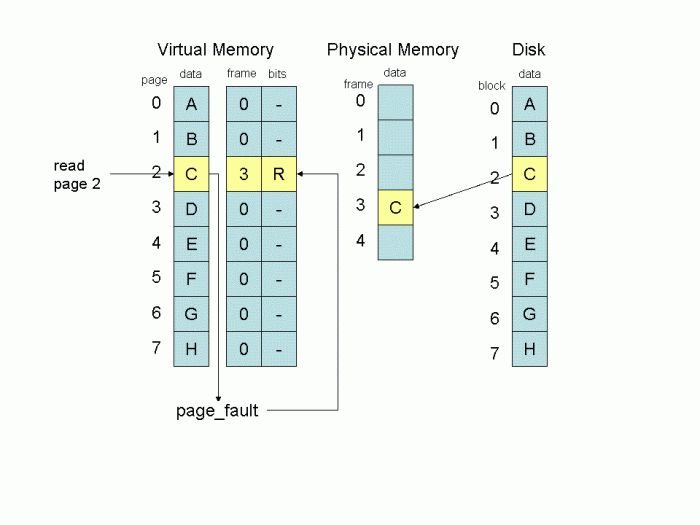
Virtual memory is commonly implemented by demand paging, which means a page is bought into the memory when it is required. Under this concept Each address generated by a program is considered virtual. It must be translated to a real physical address and if the real address is not there in the memory then it is page fault and corresponding page is bought into the physical memory. See the following image which clarify the complete scenario ...