The Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS) is the kernel of Cisco routers and most switches.A kernel is the basic, necessary part of an operating system that allocates resources and manages things such as low-level hardware interface and security.
Cisco Router IOS:
The Cisco IOS is the proprietary kernel that provides routing, switching, internetworking, and telecommunication features. The first IOS was written by William Yeager in 1986, and it enabled networked applications. It run on most Cisco routers as well as an ever-increasing number of Cisco Catalyst Switches, like the Catalyst 2950/2960 and 3550/3560 series Switches.
Some important things that the Cisco router IOS software is responsible for :
* Carrying network protocol and functions.
* Connecting high-speed traffic between devices.
* Adding security to control access and stop unauthorized network use.
* Providing scalability for ease of network growth and redundancy.
* Supplying network reliability for connecting to network resources.
Admin can access the Cisco IOS through the console port of a router from modem into the auxiliary (or Aux) port , or even through Telnet, Access to the IOS command line is called an EXEC session.
Connecting to Cisco Router:
User can connect to a Cisco router to configure it, verify its configuration, and check statistics. there are different way to do this. the first user would connect to the console port.
The console port is usually an RJ-45 (8-pin modular) connection located at the back of the router—by default, there’s may or may not be a password set. The new ISR routers **use Cisco as the username and cisco as the password by default.
Admin can also connect to a Cisco router through an auxiliary port—which is really the same
thing as a console port, so it follows that you can use it as one. But an auxiliary port also
allows you to configure modem commands so that a modem can be connected to the router.
This is a cool feature—it lets you dial up a remote router and attach to the auxiliary port if the
router is down and you need to configure it
out-of-band(meaning out of the network).
The third way to connect to a Cisco router is in-band, through the program Telnet.
(In-band means configuring the router through the network, the opposite of "out-of-band.")Telnet is a terminal emulation program that acts as though it’s a dumb terminal. You can use Telnet to
connect to any active interface on a router, such as an Ethernet or serial port.
Figure shows an illustration of a Cisco 2600 series modular router, which is a cut above
routers populating the 2500 series because it has a faster processor and can handle many more
interfaces. Both the 2500 and 2600 series routers are end of life (EOL), and you can only buy
them used. However, many 2600 series routers are still found in production, so it’s important
to understand them. Pay close attention to all the different kinds of interfaces and connections.
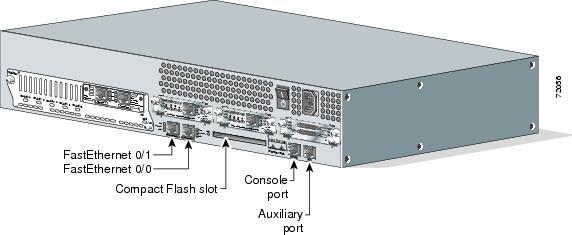
The 2600 series router can have multiple serial interfaces, which can be used for connecting
a T1 or Frame Relay using a serial V.35 WAN connection. Multiple Ethernet or FastEthernet
ports can be used on the router, depending on the model. This router also has one console and
one auxiliary connection via RJ-45 connectors.
Another router I want to talk about is the 2800 series (shown in Figure). This router has
replaced the 2600 series router series and is referred to as an Integrated Services Router (ISR).
It gets its name because many of the services, like security, are built into it. It’s a modular
device like the 2600, but it’s much faster and a lot more sleek—it’s elegantly designed to support
a broad new range of interface options.
