J2EE (Java Enterprise Edition) follows the distributed multi-tiered application approach which means the entire application may not reside at a single location, but distributed. And the applications is divided into various tiers. J2ee application is composed of various components which can be created by the different developers and then assembled together. These components can be installed on different machines across various tiers. And the distribution of application components across the solely different tiers depends upon the functionality it performs.
JEE Architecture Diagram
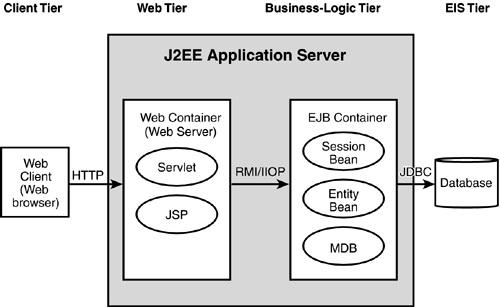
J2EE application tiers are as follows
Client Tier (Web Browser or any other kinds of clients)
Web tier
Business Tier
Enterprise Information tier (Database or sometimes XMLs or flatfiles)
Various JEE Components
Components are self contained piece of software that are reusable across applications and are configurable external to the source code.
J2EE components are of three types : client component, web component and business component. The client components interact with the user, the web components interact with the web browsers using the HTTP protocol, and the business components interact with the application server and execute the business logic.
Client component of JEE architecture
Client components is of two types : web client and application client.
A web client, generally a browser, sends a request to the server and renders the webpage sent back by the server. However, it may not perform any complex tasks such as querying a database or performing any complicated business tasks and hence is also referred to as thin client. The complex tasks are performed on the server. For displaying web pages with applets, the web clients may require Java plug-ins and security policy files for executing the applets.
An application client is a standalone application that doesn’t run in browsers. It can access components in the business tier directly. Note that web clients that require access to a servlet running in the Web tier can open an HTTP connection with the servlet.
Web component of JEE architecture
Web components for java are Servlets and JavaServer Pages (JSP). A servlet receives HTTP requests from the client, processes them, and returns the output. It can also generate dynamic responses. Similar to servlets, JSP also create dynamic web pages. JSP pages are converted into servlets and executed within a servlet container. They are used to display the results processed by a servlet.
Business component of JEE architecture
Business components implement the business logic or the functional process logic that defines the business rules and constraints. For example business process such as withdrawing amount from the bank. Business components are of three types : session beans, entity beans, and message-driven beans. Session beans represent a session with a client. Being a transient object, they lose their data on completion of the session. On the other hand, entity beans are persistent objects and so retain data even after the session. They represent a row of data in a database table. Message-driven beans are for receiving the receiving Java Message Service (JMS) messages asynchronously.
